The health of your gums (gingiva) is vital to complete oral health. Preventive prophylactic cleanings maintain healthy tissue. Scaling and root planing (deep cleanse) treat unhealthy gums, which untreated, may lead to tooth loss or mobility. Bleeding when brushing and flossing, mineral buildup (calculus), and bad breath are signs of unhealthy gums.

Periodontics involves the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of periodontal disease.
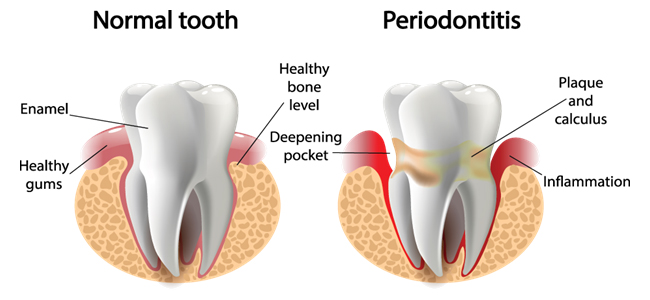
Periodontal disease, also known as gum disease, is an inflammation and infection of the gum tissues. It includes the stages commonly known as gingivitis and periodontitis. Periodontal disease is the leading cause of tooth loss in adults.
When plaque and tartar are left untreated on teeth and gums, gum disease may develop. You can reduce your risk of gum disease by brushing twice and flossing once every day. You should also have a dental exam and professional cleaning at least twice each year.
Gingivitis includes a variety mild to moderate symptoms, such as:
- Red, swollen gums
- Sensitive teeth
- Gums bleeding from normal brushing or eating
- Chronic halitosis (bad breath)
- Difficulty or pain chewing
Periodontitis is a more advanced form of gum disease. In this case, gums begin to pull away from teeth, creating small “pockets” along the gum line. Tooth loss, bone loss, and damage to gums and soft tissues can occur with periodontitis.
The most common treatment for gum disease is known as deep cleaning or scaling and root planing. Our hygienist can perform this gentle and effective removal of tartar, calculus, and infected tissue.
Common risk factors for gum disease include poor oral hygiene habits, diabetes, smoking, and hormonal changes. Some medications can also increase your likelihood of developing gum disease. Many recent studies have found that untreated gum disease negatively impacts other aspects of your overall health. This is especially common for patients with cardiovascular disease or diabetes.
Comprehensive periodontal maintenance and care protects not only your gingival health, but also works to prevent tooth loss and reduce serious risks to your overall health as well. When allowed to flourish, the harmful bacteria responsible for gum disease can erode bone density and even enter your bloodstream, causing health issues in other areas of the body. Potential benefits of periodontal care include:
- Remove plaque buildup along the gum line, between teeth, and within the pockets surrounding the roots of each tooth
- Eliminate bacteria and infection from the gums
- Heal gingival pockets and reduce pocket depth
- Reduce gum pain, bleeding, inflammation, and/or redness
- Resolve persistent bad breath related to active disease
- Reduce the risk of heart disease and the spread of infection to other areas of the body
- Protect teeth and jawbone density
Scaling and root planing, also called a deep cleaning, is typically the initial phase of therapy for any stage of periodontal disease. The procedure involves physically removing plaque, tartar, bacteria, and other buildup from the teeth and along the roots within the gingival pockets. Local anesthetic is used to numb the gums during the cleaning process to reduce any significant discomfort. Once scaling and planing is complete, Doctors may recommend an antimicrobial rinse to attack any remaining bacteria. For patients with deep infected pockets, Arestin®—a time-released antibiotic—can be administered to affected areas to continuously fight bacteria for up to 21 days.
Timely, effective periodontal treatment can prevent both the development and progress of gum disease. Patients who undergo these therapies at our practice typically report a dramatic reduction in pain and a marked improvement in the appearance of their gums. For the best long-term results, patients are encouraged to keep up with proper daily dental hygiene (brushing and flossing) and attend regularly scheduled dental appointments.
Periodontics is a dental specialty that deals in the treatment of the gum tissue supporting the teeth.
Periodontal disease or gum disease is an infection of bone and the supporting structures of your teeth. It is estimated that 80% of the adult population has gum disease to one degree or another.
Periodontal bacteria can cause an inflammatory reaction which leads to the destruction of the fibers that connect teeth to bone and can create a space called a periodontal pocket. While everyone has some amount of pocketing, the normal depths are 1 to 3 mm. You can keep 3 mm or less pockets clean by yourself with routine brushing and flossing. However, in situations of periodontal disease, the pockets are deeper than 3 mm and it is impossible for you to clean and maintain them. As a result, bacteria and debris exist at the bottom of the pocket which leads to chronic gum infection. As we age, we become more susceptible to periodontal bacteria and lack of proper hygiene or cleaning is another reason for periodontal disease. Without treatment, teeth will lose enough support to become loose and painful and eventually will be lost.
Gum disease not only affects the gums and inside your mouth, but also affects your entire body! If you have gum disease you are also running the risk of many other much worse problems such as: stroke, heart disease, lung disease, diabetes, gastric ulcers, osteoporosis and preterm babies.
The only way to prevent problems like these from occurring is to care for your gums.
Gingivitis
Gingivitis is an early stage of gum disease. Gums become tender, swollen and likely to bleed. This generally can be stopped with proper oral hygiene and treatment from your dentist.
Moderate Periodontitis
At the moderate stage of gum disease, the gums deteriorate and begin detaching themselves from the teeth forming gum pockets, which allows plaque to collect below the gum line. This causes tooth roots to become susceptible to decay.
Advanced Periodontitis
This is an advanced stage of gum tissue and bone loss. Teeth become loose and may even need to be extracted. This causes difficulties in normal everyday chewing and biting. If advanced periodontal disease is left untreated, patients run the risk of other serious health problems.
Tooth Scaling
Scaling is necessary when plaque and tartar are detected at or below the gum line. Plaque and tartar are then scraped off the tooth’s crown and root.
Routine cleanings and examinations are the best defense against dental disease
Root Planing
In many cases, the tooth’s surface is smoothed by root planing after scaling.
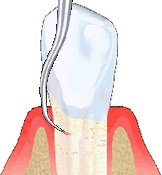
Scaling and root planing are non-surgical procedures in which the hygienist removes plaque and tartar from below the gum line. Root surfaces are cleaned and smoothed with specially designed instruments. It is important to remove the plaque and tartar from the pockets. Bacterial toxins irritate the gums, and plaque and the rough surfaces of tartar are a breeding ground for bacteria.
Medication
Antibiotics or irrigation with antimicrobials (chemical agents or mouth rinses)may also be required to help control the growth of bacteria that create toxins and cause periodontitis.
Tissue Graft
Often gum tissues around the necks of the teeth recede due to periodontal disease, genetically thin tissue, or aggressive oral hygiene. As a result of recession, tooth roots often become sensitive to cold. We can perform a variety of periodontal tissue augmentation procedures which can cover sensitive or unaesthetic root exposures. In addition to improving aesthetics, tissue grafting procedures provide a thicker band of tissue around the necks of treated teeth which improves long-term prognosis.
Your teeth may actually be the proper lengths, but they are covered with too much gum tissue. Gingivectomy is a procedure to correct this condition.
During this procedure, excess gum and bone tissue are re-shaped to expose more of the natural tooth. This can be done to one tooth, to even your gum line, or to several teeth to expose a natural, broad smile.
Specialists can perform periodontal plastic surgical procedures to replace missing gum tissue with grafting procedures. In the past this procedure required that a piece of tissue be harvested from the roof of the mouth to serve as graft material.
Unfortunately, not everyone has enough tissue available or wants to have tissue taken from this sensitive area.